J & T Capital Watch... Exploring labor outsourcing and labor dispatch from the perspective of IPO audit.
Published:
2021-12-16
In practice, most of the proposed IPO enterprises have more or less labor problems, and with more and more enterprises adopting the labor outsourcing model, the CSRC is paying more and more attention to the labor outsourcing problem. This paper summarizes the difference between labor outsourcing and labor dispatch, and analyzes the focus of the audit of labor outsourcing and labor dispatch by the regulatory authorities in the IPO, with a view to learning and discussing with you. 1. what is labor outsourcing? Labor outsourcing refers to the business outsourcing mode in which an enterprise contracts part of its business or function to the relevant labor service organization, and the labor service organization arranges the labor service personnel to complete the corresponding business or work according to the specific needs of the enterprise. Under the labor outsourcing mode, there is no actual employment relationship between the enterprise and the worker, so there is no need to bear the obligations of the employer. To some extent, labor outsourcing can save the labor cost of the enterprise and reconfigure the various resources of the enterprise according to the business characteristics of the enterprise. Its basic legal relationship is shown in the following figure: In the June 2020 revision of the CSRC's "Questions and Answers to Certain Questions on Initial Business", question 47 answers the situation related to the outsourcing of labor services of the initial enterprise: "Question 47, the outsourcing of labor services of the initial enterprise, what aspects should the intermediary focus on? A: Some of the first-time enterprises have handed over more labor activities to specialized labor outsourcing companies for implementation. Intermediary agencies should pay full attention to the following aspects:(1) the legal compliance of the labor service companies, such as whether they are independent entities, whether they have the necessary professional qualifications, whether the business implementation and personnel management comply with relevant laws and regulations, the background of the business transactions between the issuer and the issuer and whether there are major risks;(2) whether the labor service company specializes or mainly serves the issuer, if there is a situation that mainly serves the issuer, attention should be paid to its reasonableness and necessity, and whether the identification and disclosure of related relationships are true, accurate and complete. Intermediary agencies shall check such situations according to the relevant requirements of related parties from the perspective of substance over form, and especially consider the impact of their operating results on the issuer's financial data and whether the issuer meets the issuance conditions;(3) The composition and changes of the labor service company, the main contents of the labor service outsourcing contract, whether the changes in the number of labor services and expenses match the issuer's operating performance, whether the pricing of labor costs is fair and whether there is an inter-period accounting situation. Intermediaries should make full arguments on the above aspects and express clear opinions." In recent years, when the CSRC approves the listing of enterprises, many enterprises are required to disclose or explain the outsourcing of labor services in their feedback. We are concerned that the main businesses of these enterprises that are required to give feedback on labor outsourcing are different, and the industries are distributed in the fields of construction, building materials and chemical industry, computer, logistics and transportation. In general, the outsourcing is mostly engineering construction work, and it is non-critical and auxiliary business. The primary concern of the CSRC is whether the intermediary agencies disclose the labor outsourcing truthfully, especially when the labor outsourcing costs account for a relatively high proportion or pose a significant risk to the issuer's business, the intermediary agencies are required to disclose the relevant information in detail according to the principle of "substance is more important than form", not only the specific situation of the labor outsourcing business and the reasons for outsourcing, the specific circumstances of the labor outsourcing unit should also be disclosed. 2. what is labor dispatch? According to the provisions of the the People's Republic of China Labor Contract Law (2012 Amendment) and the Interim Provisions on Labor Dispatch, labor dispatch refers to the labor dispatch unit with the qualification of labor dispatch business to conclude a labor contract with the laborer, and the labor dispatch unit then signs a labor dispatch agreement with the employing unit that needs the laborer. Finally, the labor dispatch unit sends the laborer to the employing unit to work. As a flexible way of employment, labor dispatch is usually used by enterprises to solve the problem of labor shortage, which can effectively save the labor cost of labor enterprises, especially in some labor-intensive enterprises. Its basic legal relationship is shown in the following figure: The Interim Provisions on Labor Dispatch stipulate that labor dispatch can only be implemented in temporary, auxiliary or alternative jobs: temporary jobs refer to jobs that last no more than 6 months; auxiliary jobs refer to non-main business jobs that provide services for main business jobs; alternative jobs refer to a certain period of time when the workers of the employing unit are unable to work due to off-duty study, vacation and other reasons, jobs that can be replaced by other workers. And the employing unit shall strictly control the number of dispatched workers, and the number of dispatched workers shall not exceed 10% of the total number of workers. In the practice of enterprise IPO, the employment method of labor dispatch is more common in labor-intensive enterprises. At the same time, in order to prevent the issuer from failing to sign labor dispatch contracts in accordance with the law and damage the legitimate rights and interests of dispatched employees during the reporting period, in the IPO declaration process, labor dispatch is often one of the issues that regulators focus on. 3. the difference between the two and audit points From the foregoing analysis, it follows that labor dispatch is a moderate separation of employment and use, and that labor outsourcing does not involve a separation of employment and use. That is, under the employment form of labor dispatch, the employing unit transfers the right to establish labor relations, but does not transfer the right to manage things and people. The labor of workers is completed under the supervision and management of the employing unit and is managed by the employing unit. In addition, in the actual operation process, we are concerned that the regulatory authorities in the filing process of the proposed IPO enterprises on the two audit points have the following differences: 1. The common audit concerns of regulatory agencies on labor outsourcing in the IPO declaration process are as follows:(1) whether the information disclosure is sufficient;(2) Independent judgment: comprehensively judge whether the enterprise has significant dependence on labor outsourcing suppliers and analyze the impact on the independence of the issuer;(3) Internal control: pay attention to the internal control and risk control measures related to the labor outsourcing link of the issuer;(4) The determination of labor outsourcing and labor dispatch: the situation of "false outsourcing, real dispatch" is more concerned. 2. The common audit concerns of regulatory agencies on labor dispatch issues during the IPO declaration process are as follows:(1) Whether the labor dispatch unit has an associated relationship with the issuer, and whether the related transactions are legal and compliant;(2) Whether all links of labor dispatch comply with The provisions of laws and regulations, whether there are circumstances that damage the legitimate rights and interests of workers;(3) Whether there are major violations or the risk of being punished. In summary, labor and employment compliance is an important part of corporate compliance operations and a basic requirement for companies to go public. Therefore, for the employment of enterprises, we should pay attention to the provisions of relevant laws and regulations, implement and arrange the corresponding production and operation plans in accordance with the relevant provisions of laws and regulations on labor dispatch and labor outsourcing, and not only ensure that the employment mode, number of people, posts, etc. meet the restrictions of relevant laws and regulations, but also examine the qualifications of the other party, it is not allowed to deliberately evade the obligations of the employer by means of labor dispatch or labor outsourcing. As for the intermediary agencies, they should judge the actual employment nature of the enterprise from the principle of "substance is more important than form", rather than simply judging according to the contract form signed by the enterprise. For the situation that the essence belongs to labor dispatch and there are violations, it should be regulated in time to avoid obstacles in the process of listing audit and affect the progress of listing.
In practice, most of the proposed IPO enterprises have more or less labor problems, and with more and more enterprises adopting the labor outsourcing model, the CSRC is paying more and more attention to the labor outsourcing problem. This paper summarizes the difference between labor outsourcing and labor dispatch, and analyzes the focus of the audit of labor outsourcing and labor dispatch by the regulatory authorities in the IPO, with a view to learning and discussing with you.
1. what is labor outsourcing?
Labor outsourcing refers to the business outsourcing mode in which an enterprise contracts part of its business or function to the relevant labor service organization, and the labor service organization arranges the labor service personnel to complete the corresponding business or work according to the specific needs of the enterprise. Under the labor outsourcing mode, there is no actual employment relationship between the enterprise and the worker, so there is no need to bear the obligations of the employer. To some extent, labor outsourcing can save the labor cost of the enterprise and reconfigure the various resources of the enterprise according to the business characteristics of the enterprise. Its basic legal relationship is shown in the following figure:
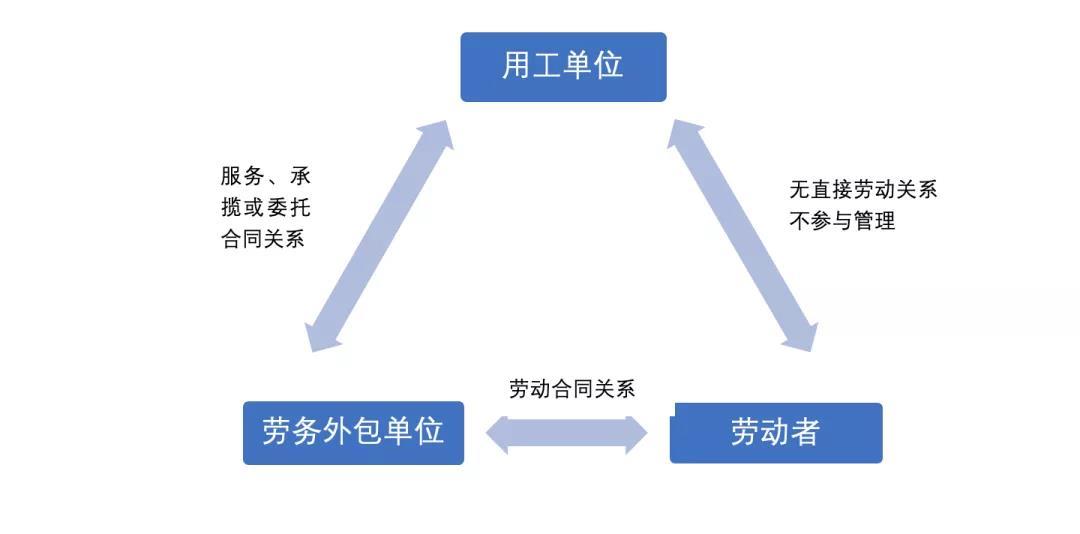
In the June 2020 revision of the CSRC's "Questions and Answers to Certain Questions on Initial Business", question 47 answers the situation related to the outsourcing of labor services of the initial enterprise: "Question 47, the outsourcing of labor services of the initial enterprise, what aspects should the intermediary focus on? A: Some of the first-time enterprises have handed over more labor activities to specialized labor outsourcing companies for implementation. Intermediary agencies should pay full attention to the following aspects:(1) the legal compliance of the labor service companies, such as whether they are independent entities, whether they have the necessary professional qualifications, whether the business implementation and personnel management comply with relevant laws and regulations, the background of the business transactions between the issuer and the issuer and whether there are major risks;(2) whether the labor service company specializes or mainly serves the issuer, if there is a situation that mainly serves the issuer, attention should be paid to its reasonableness and necessity, and whether the identification and disclosure of related relationships are true, accurate and complete. Intermediary agencies shall check such situations according to the relevant requirements of related parties from the perspective of substance over form, and especially consider the impact of their operating results on the issuer's financial data and whether the issuer meets the issuance conditions;(3) The composition and changes of the labor service company, the main contents of the labor service outsourcing contract, whether the changes in the number of labor services and expenses match the issuer's operating performance, whether the pricing of labor costs is fair and whether there is an inter-period accounting situation. Intermediaries should make full arguments on the above aspects and express clear opinions."
In recent years, when the CSRC approves the listing of enterprises, many enterprises are required to disclose or explain the outsourcing of labor services in their feedback. We are concerned that the main businesses of these enterprises that are required to give feedback on labor outsourcing are different, and the industries are distributed in the fields of construction, building materials and chemical industry, computer, logistics and transportation. In general, the outsourcing is mostly engineering construction work, and it is non-critical and auxiliary business. The primary concern of the CSRC is whether the intermediary agencies disclose the labor outsourcing truthfully, especially when the labor outsourcing costs account for a relatively high proportion or pose a significant risk to the issuer's business, the intermediary agencies are required to disclose the relevant information in detail according to the principle of "substance is more important than form", not only the specific situation of the labor outsourcing business and the reasons for outsourcing, the specific circumstances of the labor outsourcing unit should also be disclosed.
2. what is labor dispatch?
According to the provisions of the the People's Republic of China Labor Contract Law (2012 Amendment) and the Interim Provisions on Labor Dispatch, labor dispatch refers to the labor dispatch unit with the qualification of labor dispatch business to conclude a labor contract with the laborer, and the labor dispatch unit then signs a labor dispatch agreement with the employing unit that needs the laborer. Finally, the labor dispatch unit sends the laborer to the employing unit to work. As a flexible way of employment, labor dispatch is usually used by enterprises to solve the problem of labor shortage, which can effectively save the labor cost of labor enterprises, especially in some labor-intensive enterprises. Its basic legal relationship is shown in the following figure:
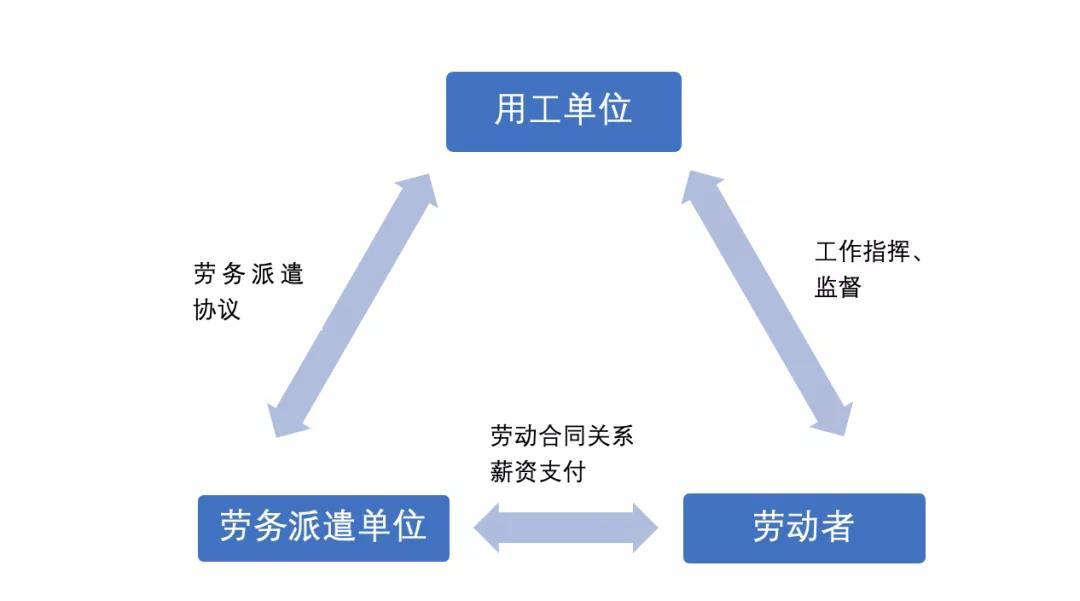
The Interim Provisions on Labor Dispatch stipulate that labor dispatch can only be implemented in temporary, auxiliary or alternative jobs: temporary jobs refer to jobs that last no more than 6 months; auxiliary jobs refer to non-main business jobs that provide services for main business jobs; alternative jobs refer to a certain period of time when the workers of the employing unit are unable to work due to off-duty study, vacation and other reasons, jobs that can be replaced by other workers. And the employing unit shall strictly control the number of dispatched workers, and the number of dispatched workers shall not exceed 10% of the total number of workers. In the practice of enterprise IPO, the employment method of labor dispatch is more common in labor-intensive enterprises. At the same time, in order to prevent the issuer from failing to sign labor dispatch contracts in accordance with the law and damage the legitimate rights and interests of dispatched employees during the reporting period, in the IPO declaration process, labor dispatch is often one of the issues that regulators focus on.
3. the difference between the two and audit points
From the foregoing analysis, it follows that labor dispatch is a moderate separation of employment and use, and that labor outsourcing does not involve a separation of employment and use. That is, under the employment form of labor dispatch, the employing unit transfers the right to establish labor relations, but does not transfer the right to manage things and people. The labor of workers is completed under the supervision and management of the employing unit and is managed by the employing unit. In addition, in the actual operation process, we are concerned that the regulatory authorities in the filing process of the proposed IPO enterprises on the two audit points have the following differences:
1. The common audit concerns of regulatory agencies on labor outsourcing in the IPO declaration process are as follows:(1) whether the information disclosure is sufficient;(2) Independent judgment: comprehensively judge whether the enterprise has significant dependence on labor outsourcing suppliers and analyze the impact on the independence of the issuer;(3) Internal control: pay attention to the internal control and risk control measures related to the labor outsourcing link of the issuer;(4) The determination of labor outsourcing and labor dispatch: the situation of "false outsourcing, real dispatch" is more concerned.
2. The common audit concerns of regulatory agencies on labor dispatch issues during the IPO declaration process are as follows:(1) Whether the labor dispatch unit has an associated relationship with the issuer, and whether the related transactions are legal and compliant;(2) Whether all links of labor dispatch comply with The provisions of laws and regulations, whether there are circumstances that damage the legitimate rights and interests of workers;(3) Whether there are major violations or the risk of being punished.
In summary, labor and employment compliance is an important part of corporate compliance operations and a basic requirement for companies to go public. Therefore, for the employment of enterprises, we should pay attention to the provisions of relevant laws and regulations, implement and arrange the corresponding production and operation plans in accordance with the relevant provisions of laws and regulations on labor dispatch and labor outsourcing, and not only ensure that the employment mode, number of people, posts, etc. meet the restrictions of relevant laws and regulations, but also examine the qualifications of the other party, it is not allowed to deliberately evade the obligations of the employer by means of labor dispatch or labor outsourcing. As for the intermediary agencies, they should judge the actual employment nature of the enterprise from the principle of "substance is more important than form", rather than simply judging according to the contract form signed by the enterprise. For the situation that the essence belongs to labor dispatch and there are violations, it should be regulated in time to avoid obstacles in the process of listing audit and affect the progress of listing.
Key words:
Related News

Zhongcheng Qingtai Jinan Region
Address: Floor 55-57, Jinan China Resources Center, 11111 Jingshi Road, Lixia District, Jinan City, Shandong Province



